
Applicable To. Intrapartum hemorrhage (excessive) associated with afibrinogenemia; Intrapartum hemorrhage (excessive) associated …


INTRODUCTION. Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is the second most common cause of stroke, following ischemic stroke. Mortality and morbidity is high.



Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate) 0.2 Mg Tablets for the treatment and prevention of uterine hemorrhage. The only FDA-approved oral uterotonic.
There are two main types of hemorrhagic stroke: Intracerebral hemorrhage, which is basically bleeding within the brain itself (when an artery in the brain bursts, flooding the surrounding tissue with blood), due to either intraparenchymal hemorrhage (bleeding within the brain tissue) or intraventricular hemorrhage (bleeding within the brain’s
Side Effects. Drug information provided by: Micromedex Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.

Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association
WebMD explains the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment of a brain hemorrhage.
Eisai Co., Ltd. 1 . Revised: April 2018 (26th version) Standard Commodity Classification No. of Japan 873332. Oral anticoagulant – Warfarin potassium tablets, JP – …
Bleeding, also known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging, is blood escaping from the circulatory system. Bleeding can occur internally, where blood leaks from blood vessels inside the body, or externally, either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a break in the skin.
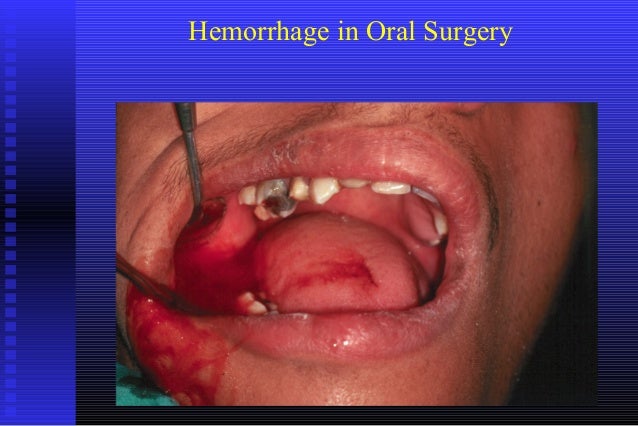
INTRODUCTION. Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is an obstetric emergency. It is one of the top five causes of maternal mortality in both high and low per capita income countries, although the absolute risk of death from PPH is much lower in high-income countries.