An ethnic group, or an ethnicity, is a category of people who identify with each other based on similarities such as common ancestry, language, history, society, culture or …
44 Nationalism, Patriotism, and Group Loyalty Although granting that nationalism is a political, economic, and sociological phenomenon, it becomes a social-psychological phenomenon to the extent that
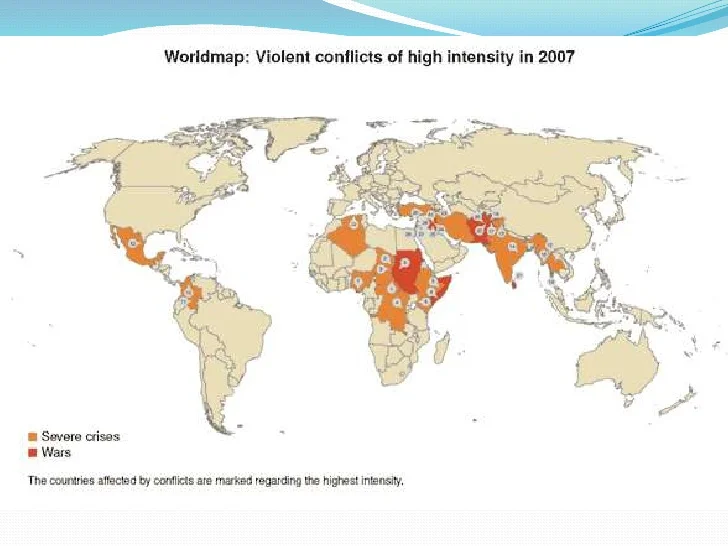
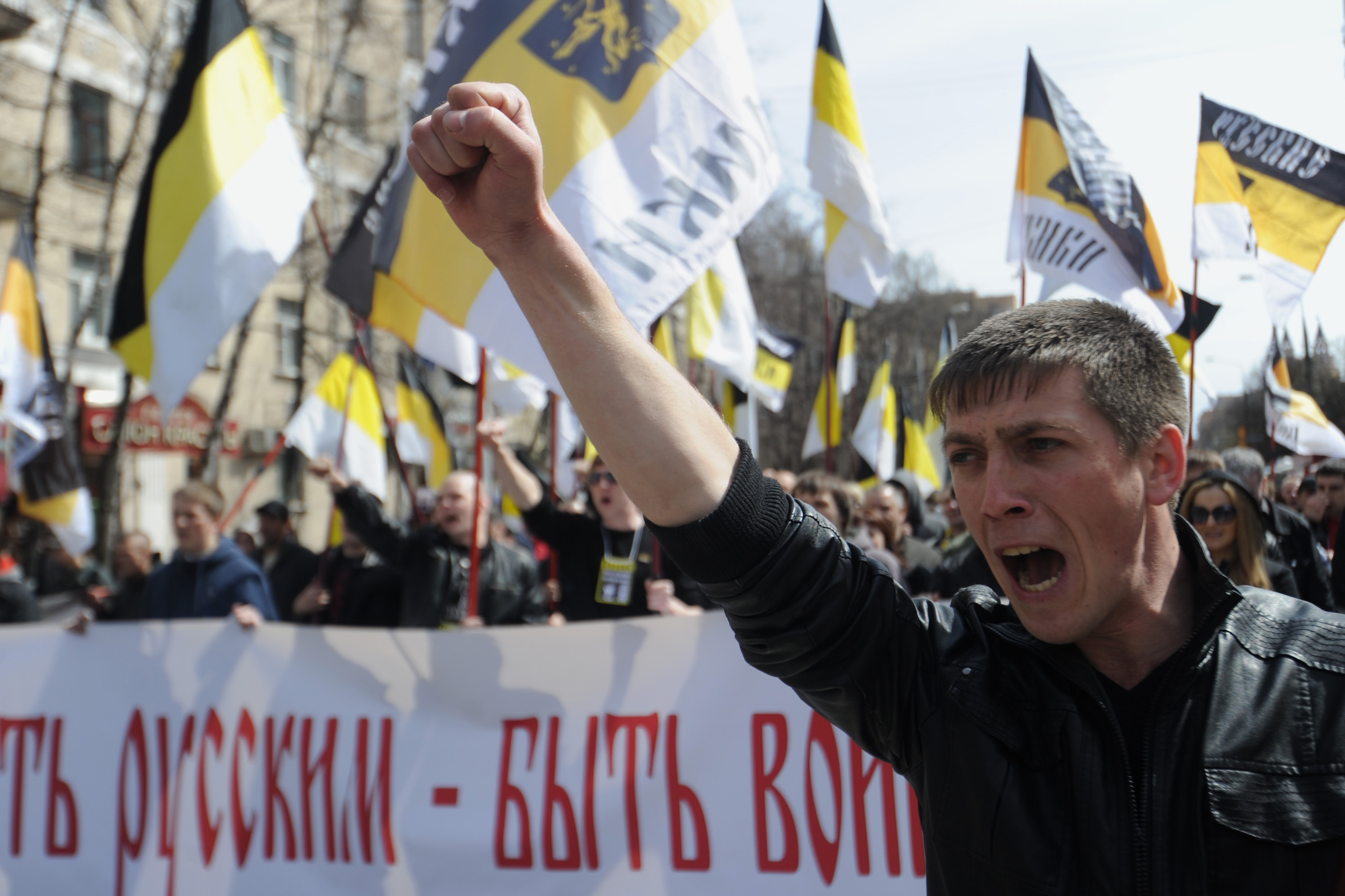
Ethnic identity, ethnicity, and ethnic group. The terms ethnic and ethnicity have their roots in the Greek word ethnos, which describes a community of common descent. In ethnic conflict research, the terms ethnic group, communal group, ethnic community, people, and ity are mostly used interchangeably.
Article on the history and contemporary characteristics of assimilation and ethnic identity formation among Asian Americans, including summaries of various theories of assimilation.


International Centre for Ethnic Studies (ICES) ජනවාර්ගික අධ්යයනය සඳහා වූ ජාත්යන්තර කේන්ද්රය

Find the right program for you. Choose from more than 80 semester and summer programs that reach more than 60 countries and address today’s most pressing issues.


National identity is one’s identity or sense of belonging to one state or to one nation. It is the sense of a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, language and politics.



the religious aspects of the Yugoslavia – Kosovo conflict. Was the Kosovo crisis an ethnic conflict or a religious conflict? There have been a series of struggles for independence during the 1990’s in the area once covered by the country of Yugoslavia: This series started in 1990 in Slovenia; 1991 in Croatia; 1992 in Bosnia Herzegovina.
Protecting wealth and privilege “The introduction in 1933 of a mandatory identity card system deepened social divisions. Every Rwandan citizen was obliged to carry the card. which stated his name and ethnic identity, i.e. Tutsi, Hutu or Twa.
5 project of disaggregation is not yet complete, as analysis of intra-ethnic remains entirely absent from the cross-national quantitative literature on civil conflict.
